If you ever wondered how Google knows which pages to show on the first and which on the second page when you search for something online, this guide will go into it in great detail. Besides learning how it all works, I want to show you how to build a crawler bot yourself using various methods. With complete control, you can implement everything with code, but modern web crawlers utilize advanced AI features and are significantly more efficient at the task at hand.
By the end of the article, you will get a good grasp of:
- What is a Crawler Bot?
- How does a Web Crawler Bot Work?
- How to Build a Web Crawler Bot? Two Main Methods
- How to prevent crawling bots from crawling your site
What is a Crawler Bot?
The core functionality of a crawler bot (also known as a spider bot) is an automated software that systematically browses the World Wide Web. It is used by Search Engines like Google to download and index all the webpages on the internet.
Now, with the rise of the AI Revolution, crawler bots are also equipped with new AI functions. Google is not the only one using spider bot web crawlers. Other popular AI-first companies, such as PerplexityBot, ClaudeBot, and GPTBot by OpenAI, are also heavily relying on them.
There are various crawler bots used for different purposes. Here are the main categories:
- Common crawler bots: Bots that respect robots.txt and automatically crawl web pages.
- Special-case crawler bots: These are used similarly to common crawler bots but are adjusted for specific products. Google has a particular AdsBot tailored for crawling ads, e.g.
- User-triggered crawler bots: Users can also trigger bots to fetch specific webpages or product information. An example of it is Google Site Verifier.
Using crawler bots is essential, as bots conduct a record high 51% of internet activity in 2025. Advanced methods and AI-powered bots are now emerging, and for the first time in history, they make up the majority of the internet, according to Imperva’s 2025 Bad Bot Report.
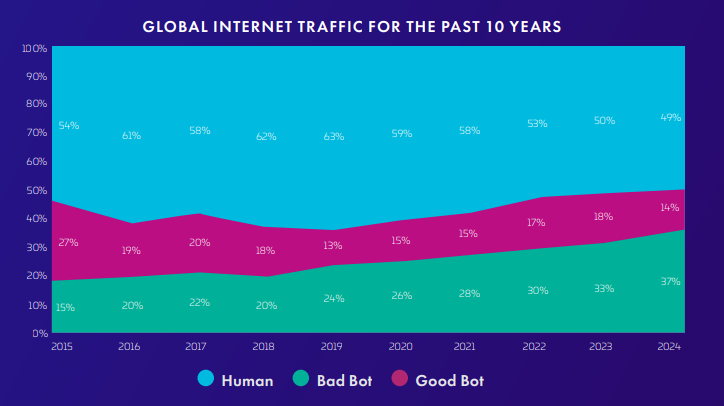
The report also states that crawler bots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and numerous malicious actors have utilized them to target websites. Approximately 37% of internet traffic is comprised of malicious bots, which target APIs, exploit business logic, and lead to a high level of fraud.
This threat is serious, and that is why I will also dedicate a part of this reading to preventing bots from crawling your site.
How does a Web Crawler Bot Work?
A crawler bot starts with the root web pages (seed list) and parses the HTML structure, looking for linked URLs. The goal of crawler bots is to discover content, which is what they do. The page is analyzed for metadata, including content quality and relevance, and then indexed. That is how it begins, building a web of pages connected and linking from one to another. This process is repetitive, starting again once a new page is fetched from the connecting hyperlinks.
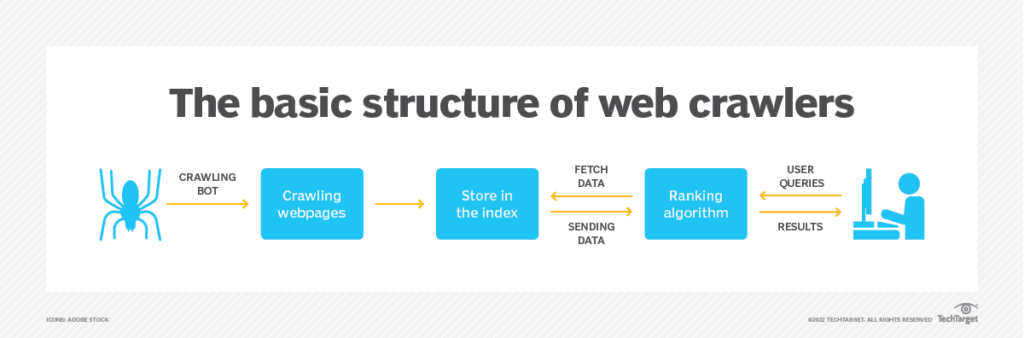
Crawler bots do not follow every link. Instead, they filter and evaluate relevant content and valid webpages. They check robots.txt to ensure they follow the crawling rules of every website as well.
As you know, the Internet is like a black hole with seemingly infinite space, so that no crawler bot can handle such a scale. For that reason, they prioritize pages while crawling to make the process as performant as possible. These are the rules and crawling policies that crawling bots follow:
- Selection Policy: While crawling, the crawling bot determines which links are most important based on PageRank or topic relevance.
- Revisit Policy: Certain pages are worth revisiting to update the index, so the crawler bot determines when.
- Politeness Policy: Crawler bots are subject to automatic delays to prevent server overloads.
- Robots.txt Compliance: Before even crawling a website, respecting the rules of robots.txt is a crucial step, as it defines which parts are off-limits.
Why You Might Want to Build a Crawler Bot
While large organizations utilize spider crawling bots for extensive operations, these tools are also highly valuable in specialized industries. Professionals frequently customize crawler bots to address the specific needs of their field. Below are some of the most potent and widespread applications:
- Content Aggregation: Exploring new content strategies and identifying the connections between various websites is a valuable tactic that many professionals use when web crawling.
- Lead Generation: Building targeted contacts by crawling business information and professionals across social media networks, such as LinkedIn, has never been easier.
- Market and Price Tracking: Conducting in-depth research on the market and its products can help you navigate the right direction on how and when to enter the market.
- SEO and Site Auditing: With numerous competitors in every industry, evaluating your business’s ranking is crucial.
How to Build a Web Crawler Bot: Two Main Methods
When you want to build a web crawler bot, you can either build one from scratch using Python scripts and libraries with complete control or use a no-code natural language tool that crawls data in seconds. Below, I provide an in-depth analysis of both approaches.
Method 1: Building with Code (Using Python)
Developers who build a crawler bot from scratch offer maximum flexibility and customization. The main disadvantage is that it requires a significant amount of time and expertise to accomplish. I will provide some pointers today on how to create a basic crawler bot, even if you have little to no programming experience.
Step 1: Install required libraries
The libraries we are using today are called BeautifulSoup and requests, and they are directly available in Python’s Package Index. BeautifulSoup directly extracts data from HTML and XML files, which are retrieved using the requests library, making HTTP requests.
After installing Python and an IDE of your choice, the command in the terminal is as follows:
Step 2: Crawler bot logic
I create a new Python file (crawler_bot.py) and start by importing the previously installed libraries.
This CrawlerBot class now requires a couple of basic functions of a crawler bot. This includes fetching to retrieve the HTML content of a page, parsing to extract data and links from the HTML page, and finally crawling to orchestrate this process.
The crawl method is iterative, utilizing a while loop that continues until the max_pages count is exhausted.
These are all part of the CrawlBot class. To run this, I finally instantiate the CrawlerBot class and provide it with simple instructions to crawl.
This is a straightforward approach to building a customized code solution for a crawler bot. Advanced methods for anti-bot detection, avoidance, or pagination are more challenging to develop and require further development. ChatGPT, as a scraper, can serve as a valuable assistant during this development process, allowing you to utilize it as a tool.
Method 2: Using a No-Code Platform
There are numerous powerful no-code crawler bots available. Still, for today’s showcasing, I will demonstrate how my personal favourite crawler bot, Chat4Data, performs compared to a fully customized, self-built solution.
Step 1: Install Chat4Data
First, I installed Chat4Data directly from the Chrome Web Store as a web crawler extension. This simplifies the process as it is already available in the browser, with direct access to all the HTML elements behind it.
Step 2: Make an account and start crawling bots
Chat4Data has a significant advantage over other crawling bot tools, as all you need to do is provide instructions in natural language, and it will crawl and scrape the data you need.
Step 3: Crawl the data like a professional
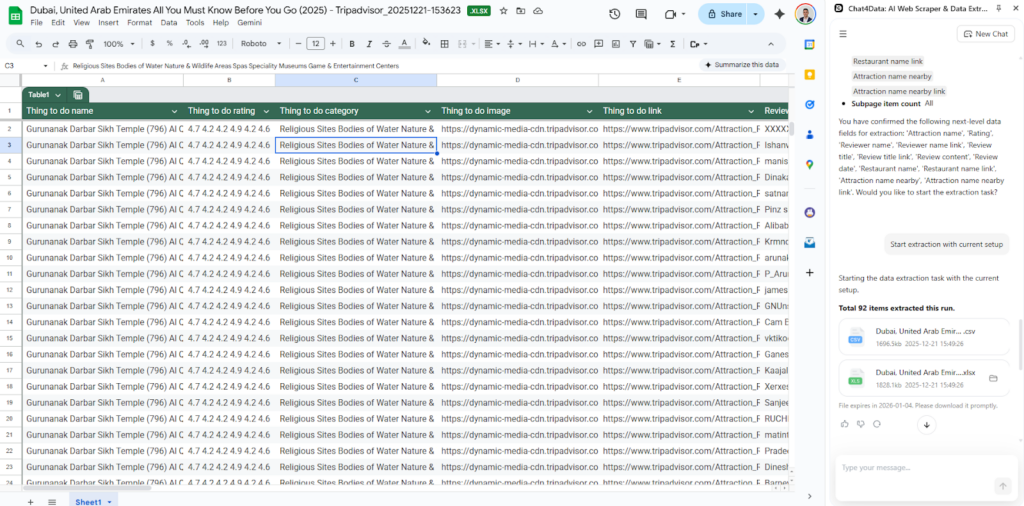
Recently, I have been considering starting a travel agency, and I want to explore the hidden gems of various cities. However, this is not easy, given the sheer number of cities in the world. I would have to know all this information to do so. That is precisely where Chat4Data steps in to help crawl this information. I will utilize TripAdvisor, which has a large dataset of various locations, pictures, and reviews. Dubai is very popular right now, so let’s see what we can find there.
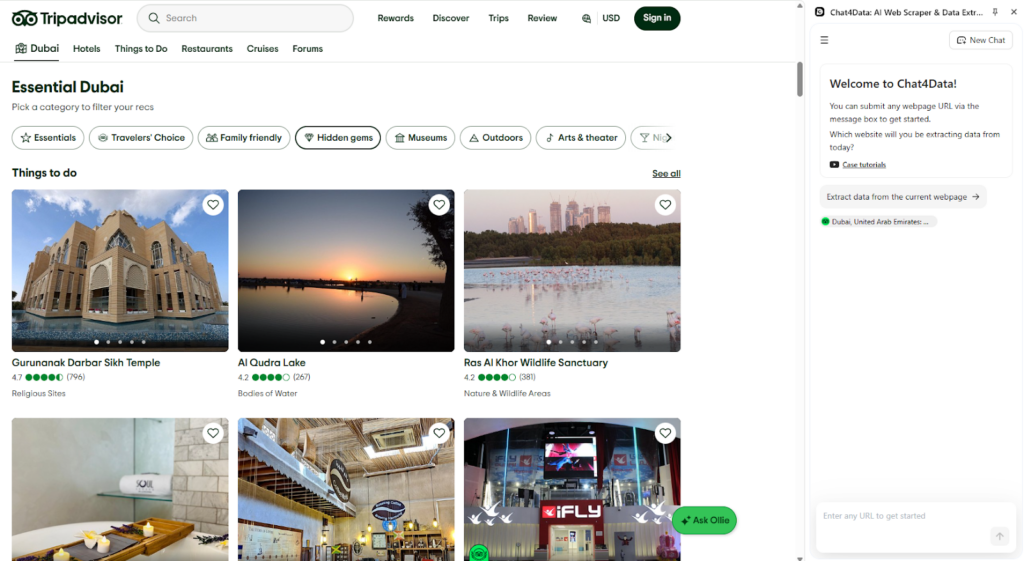
Chat4Data offers me the option to scrape the current page without requiring any further input. It’s also possible to let Chat4Data know what it should be looking for directly in the chat. Let’s try that and see what it finds. Chat4Data identified multiple categories, and although preplanned itineraries are helpful, I want to explore all the locations worth visiting.
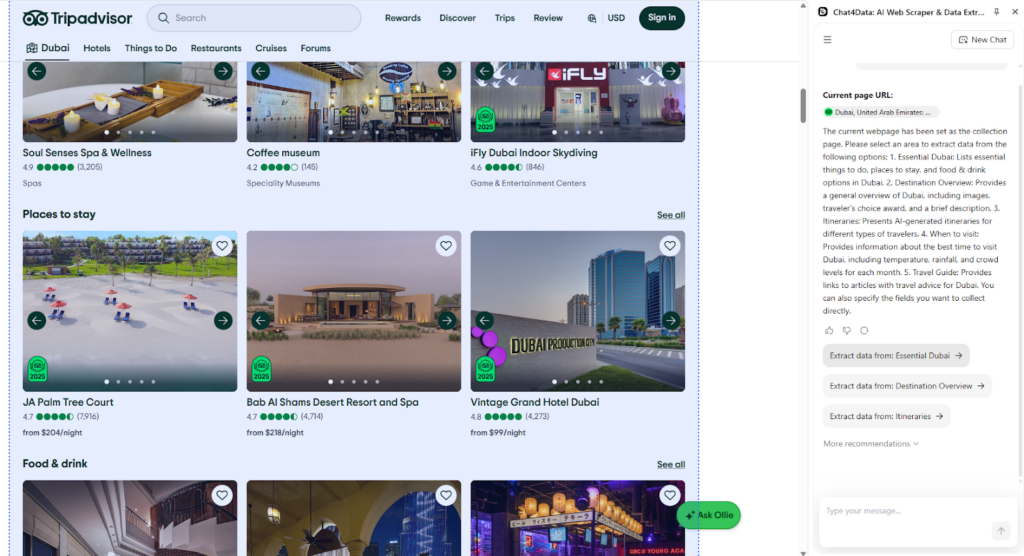
The identified data fields are categorized into distinct groups using Chat4Data’s AI features. This provides clarity in the upfront preview you get of the crawling plan. I confirm the selection, and we continue.
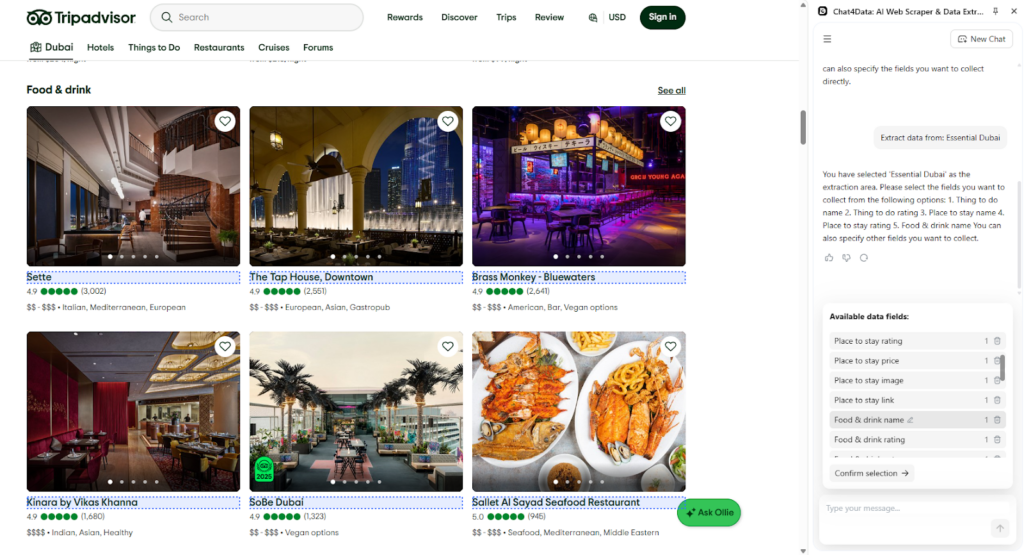
Here is where the crawling bot starts and why Chat4Data is so powerful. It automatically recognizes these as linked URLs and asks if it should also explore data from them.
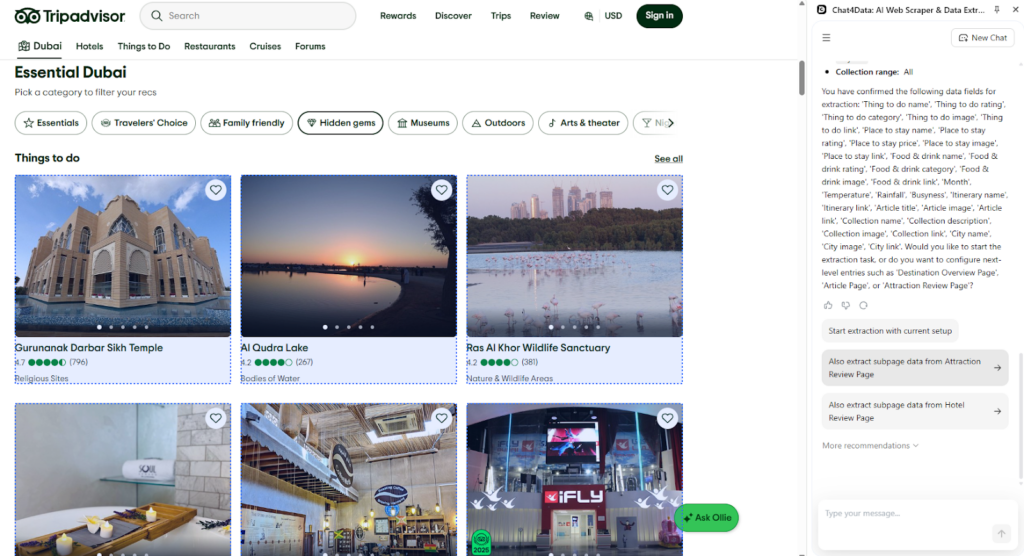
On the subpage Chat4Data, I find all sorts of information, and for me, reviews are essential because they provide a detailed description, allowing me to share them with my customers.
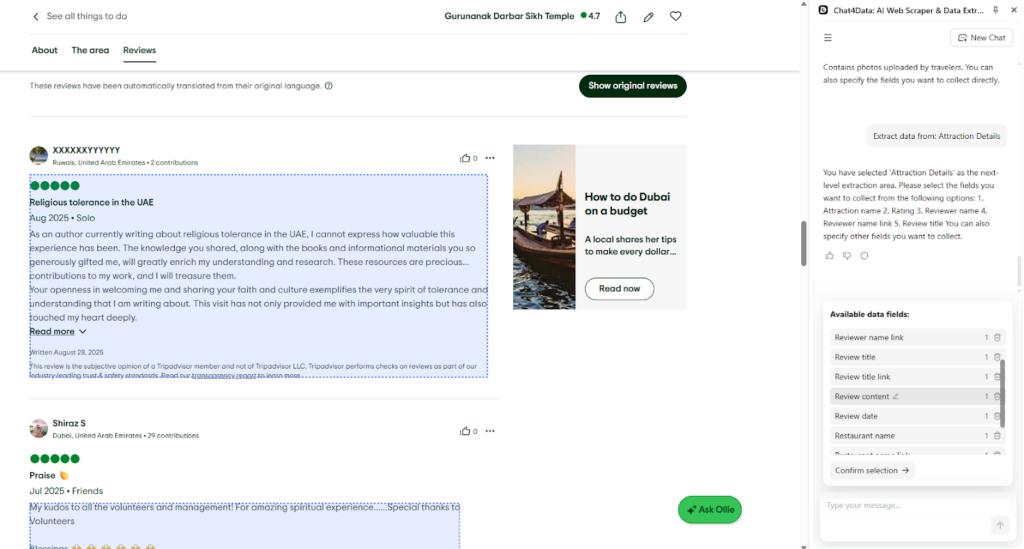
Step 4: Crawl and export data using Chat4Data
Chat4Data presents the final plan, and I start crawling the data. In a couple of minutes, all pages are automatically traversed, and I have my data ready for further processing.
How to Prevent Bots from Crawling Your Site?
Crawler bots are essential and widely used, but they also include malicious ones. In case you are looking for ways to improve the protection of a website you own from endless crawlers, here are a couple of ways to do so:
- Robots.txt rules: A set of rules that crawler bots follow is defined in robots.txt, allowing them to crawl websites respectfully and efficiently. As the owner, you can specify these rules, and most crawlers will respect them.
- Rate limiting: Servers of websites that use rate-limiting techniques to maintain their infrastructure and provide service must be protected. This method will prevent any overload of the servers and shut down the service websites that are being provided.
- JavaScript Challenges: The JavaScript challenge requires a real JavaScript engine to comply with. Professional crawler bots use these methods, and this approach is highly effective in stopping HTTP request crawler bots.
- CAPTCHA Challenges: CAPTCHA Challenges are becoming increasingly complex, making it even harder for strong algorithms to solve them. By implementing CAPTCHA on your website, you can prevent a significant amount of traffic in certain parts of your site.
- AI Bot observations: By observing clicking and scrolling patterns, anti-bot detections can strongly assume if one is a bot or not.
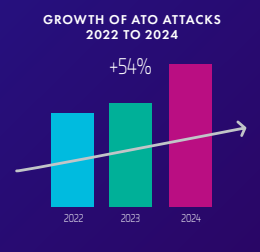
There is a growing number of Account Takeover attacks done by malicious bots. Following the steps above will provide a higher level of protection for your website and can prevent even sophisticated bad scrapers.
The AI-Powered Future: Building Crawler Bots with Chat4Data
Chat4Data has a clear advantage because it is straightforward to use with simple commands in natural language. There is no need to install anything, and it works really fast for most websites. Here are a few more advantages crawler bot Chat4Data brings over building your own web crawler bot:
- Ease of Use with Natural Language: Users simply describe the desired data, and the scraper intelligently handles the extraction process.
- Enhanced Detail with Subpage Scraping: The tool autonomously identifies and explores links and subpages, allowing for the collection of comprehensive details for each item.
- Commitment to Privacy: All operations are conducted locally, ensuring that user credentials, including those for authenticated pages, are never stored or transmitted.
Want a deeper dive? Check out these articles:
- 8 Best AI Web Scrapers in 2025
- Chat4Data vs. Instant Data Scraper
- 8 Powerful AI Crawlers for Effortless Data Extraction
- How to Power Up Your Data Collection with AI Scraping
FAQs about Crawler Bots
- What’s the difference between web crawling bots and web scraping bots?
Web crawling bots systematically browse the web to discover and list URLs. Web scraping differs in that it involves a predefined set of webpages from which it extracts specific data. When considering it, crawling is a discovery process, while scraping is a data fetching process.
- Is it legal to build a web crawler bot?
Yes, many websites offer publicly available data and are open for crawler bots. When crawling, be cautious about handling personal data and respecting each website’s privacy policies. Rules for crawling are defined in robots.txt and should be respected.
- Can I block all crawling and scraping bots from my website?
Yes, but this is not advisable. Techniques such as IP blocking or anti-bot detection can prevent unwanted traffic. However, by preventing any crawling activity, the website will be ranked very low in search engines and, in turn, harm the business or product’s popularity.
- How does an AI crawler bot Chat4Data avoid getting blocked?
With the power of AI-enhanced features, crawler bots can now avoid detection by mimicking human-like behavior. This is achieved with dynamic changes between clicks and scrolls during the crawling process. A natural pattern is shown, so there are no warnings from the websites.